Rashes to know
Conveniently located to serve Nashua, NH
Shingles
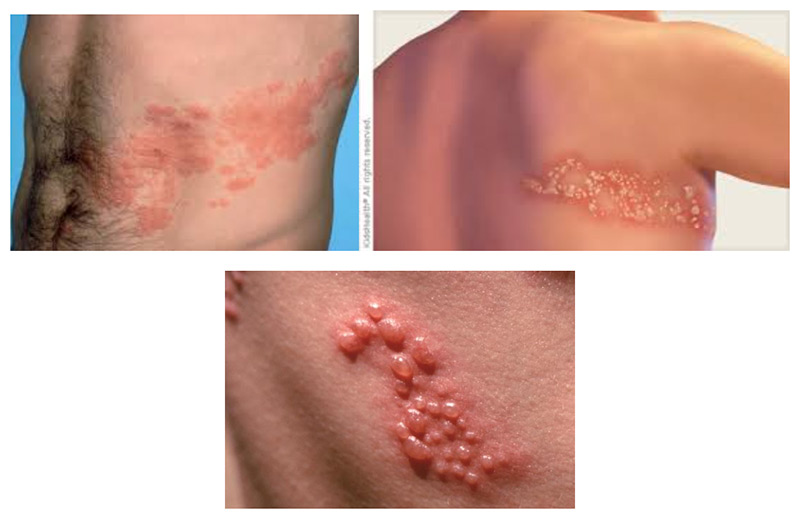
What is Shingles (Herpes Zoster)?
Shingles is a viral infection that causes a painful, blistering rash. Although shingles can occur anywhere on your body, it most often appears as a single stripe of blisters that wraps around either the left or the right side of your torso.
How do you get it?
Shingles is caused by the varicella-zoster virus — the same virus that causes chickenpox. After you’ve had chickenpox, the virus lies inactive in nerve tissue near your spinal cord and brain. Years later, the virus may reactivate as shingles.
While it isn’t a life-threatening condition, shingles can be very painful. The Center for Disease Control recommends individuals 60 years and older to receive the shingles vaccine. Vaccines can help reduce the risk of shingles, while prompt treatment can help shorten a shingles infection and lessen the chance of complications.
How do you treat it?
There’s no cure for shingles, but prompt treatment with prescription antiviral drugs can speed healing and reduce your risk of complications. These medications include:
- Acyclovir (Zovirax)
- Valacyclovir (Valtrex)
- Famciclovir (Famvir)
Shingles can cause severe pain, so your dermatologist also may prescribe:
- Capsaicin cream
- Anticonvulsants, such as gabapentin (Neurontin)
- Tricyclic antidepressants, such as amitriptyline
- Numbing agents, such as lidocaine, delivered via a cream, gel, spray or skin patch
Shingles generally lasts between two and six weeks. Most people get shingles only once, but it is possible to get it two or more times.
We appreciate the kindness with which we have been treated on each visit
…we appreciate the kindness with which we have been treated on each visit. You have a very friendly atmosphere that is felt the minute you walk into the waiting room. Don’t ever loose that human touch because it sets you apart.MW
Molluscum Contagiosum
What is molluscum contagiosum?
Molluscum contagiosum is a viral (poxvirus) infection that causes a mild skin rash. The rash looks like one or more small growths or wart-like bumps (called mollusca) that are usually pink, white, or skin-colored. The bumps are usually smooth and shiny or pearly-looking, and may have an indented center.
Molluscum contagiosum mainly affects infants and young children under the age of 10 years. It is more prevalent in warm climates than cool ones, and in overcrowded environments
How do you get it?
There are several ways it can contracted or spread:
- Direct skin-to-skin contact
- Indirect contact via shared towels or other items
- Auto-inoculation into another site by scratching or shaving
- Sexual transmission in adults
Transmission of mollusca appears to be more likely in wet conditions, such as when children bathe or swim together. The incubation period is usually about 2 weeks but can be as long as 6 months.
How do you treat it?
Regarding treatment, researchers have found that the skin often clears on its own. Clearing takes about 12 to 18 months. In many cases, children are not treated because treatment can have unwanted side effects for a child.
Procedures: Your dermatologist can perform:
- Cryosurgery: The dermatologist freezes the bumps with liquid nitrogen.
- Curettage: The dermatologist uses a small tool called a curette to scrape the bumps from the skin.
- Topical (applied to the skin) therapy: Your dermatologist can apply or prescribe various acids and blistering solutions to destroy the bumps.
Contact Dermatitis
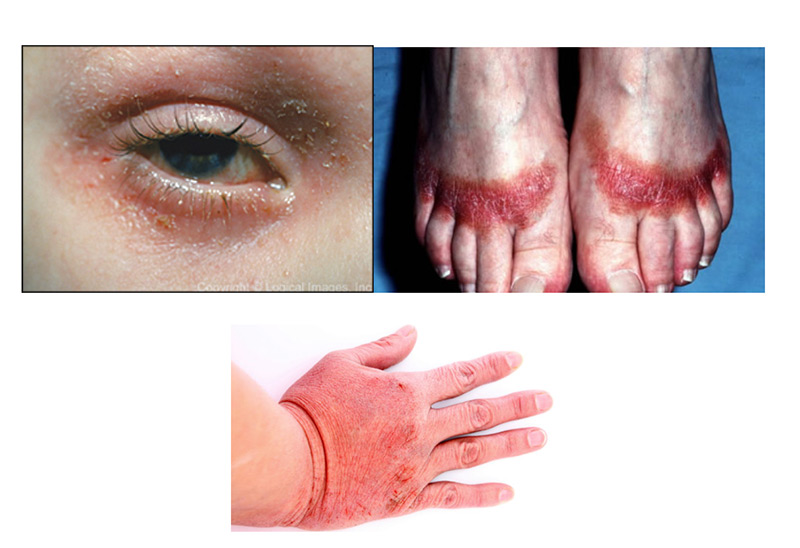
What is contact dermatitis?
Contact dermatitis refers to a group of skin disorders in which the skin reaction is due to direct contact with a causative agent. The term dermatitis implies that the outside layers of skin are affected or inflamed. It can be acute (a single episode) or chronic (persistent). Dermatitis is nearly always itchy. There are two main types of contact dermatitis, allergic and irritant.
The appearance of contact dermatitis is highly variable. It may affect any area of the body. Affected skin may have any of the following features.
- Redness
- Blisters
- Swelling
- Dryness or scaling
- Cracks (fissuring)
- Lichenification (thickened, lined skin)
- Pigmentation increased (hyperpigmentation) or reduced (hypopigmentation).
How do you get it?
Allergic contact dermatitis
Allergic contact dermatitis occurs when the skin develops an allergic reaction after being exposed to a sensitizing substance. This causes the body to release inflammatory chemicals that can make the skin feel itchy and irritated.
Common causes of allergic contact dermatitis include contact with:
- jewelry made from nickel or gold
- latex gloves
- perfumes or chemicals in cosmetics and skincare products
- poison oak or poison ivy
Irritant contact dermatitis
Irritant contact dermatitis is the most common type of contact dermatitis. It happens when the skin encounters a toxic material.
Toxic substances that can cause irritant contact dermatitis include:
- battery acid
- bleach
- drain cleaners
- kerosene
- detergents
- pepper spray
Irritant contact dermatitis can also occur when the skin comes in contact with less irritating materials like soap and water. People whose hands are frequently exposed to water, such as hairdressers, bartenders, and healthcare workers, often experience irritant contact dermatitis of the hands.
How do you treat it?
The best treatment for contact dermatitis is avoidance of the causative agent. Topical corticosteroids are the mainstay of treatment with the strength of the topical corticosteroid appropriate to the body site. If the dermatitis is severe you may be prescribed oral medication. Contact dermatitis often resolves on its own without treatment. If no resolution is achieved you may be referred to Allergist to undergo allergy testing.
Fungal infections (Ringworm)
Ringworm is a fungal skin infection that causes a red, circular, itchy rash. Ringworm is medically known as tinea or dermatophytes. Certain yeasts can also be the cause of fungal skin infections. Ringworm is referred to by other names depending on the part of the body that is affected. For example, fungal infection of the feet is athlete’s foot or tinea pedis. In the groin area, it is tinea cruris (jock itch) on the head is tinea capitis. There is fungal variant called tinea versicolor with can cause drop like patches on the skin that can look tan, white or even pink.
How do you get it?
Fungal infections can occur from skin to skin contact, contact with fungus in the environment, or from the overgrowth of normal skin flora fungus (typically yeast). This overgrowth is more commonly seen in overweight individuals who have skin to skin contact due to large skin folds. Immunocompromised individuals such as HIV patients and even diabetics can have recurrent and hard to treat infections.
How do you treat it?
Depending on the location and extent of ringworm infection, topical and/or oral antifungal medications may be prescribed for treatment. Fungal infections can be stubborn and take several weeks to months for complete resolution.





